这篇博客介绍程序实现。
程序的运行说明及命令行参数见README.md

程序实现
程序结构
程序包含如下六个类:
-
ImgProcess: 将输入图片转化为二值 -
GameState: 记录游戏棋盘及数字提示 -
Slover: 包含求解所需方法 -
SolveGame: 实际求解游戏 -
FileIO: 文件创建及读写
图像转化为游戏
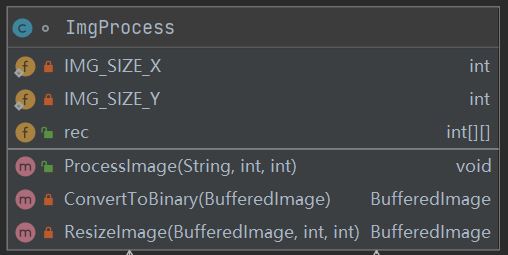
主要方法为ConvertToBinary(),逐像素处理, 根据强度I=(R+B+G)/3判断,实际中设置为R+B+G>383效果比较好,结果记录在rec[][]中。
/**
* Convert input image to binary image by comparing pixel intensity
*
* @param srcImg path of source image
* @return binary image
*/
private BufferedImage ConvertToBinary(BufferedImage srcImg) throws IOException {
rec = new int[IMG_SIZE_Y][IMG_SIZE_X];
BufferedImage binaryImg = new BufferedImage(IMG_SIZE_X, IMG_SIZE_Y, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
if (srcImg == null) {
System.out.println("No image loaded");
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < IMG_SIZE_X; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < IMG_SIZE_Y; j++) {
// Get RGB Value
int val = srcImg.getRGB(i, j);
// Convert to three separate channels
int r = (0x00ff0000 & val) >> 16;
int g = (0x0000ff00 & val) >> 8;
int b = (0x000000ff & val);
int m = (r + g + b);
// (255+255+255)/2 =283 middle of intensity
if (m >= 383) {
// for light color, set white
binaryImg.setRGB(i, j, Color.WHITE.getRGB());
} else {
// for dark color, set black
binaryImg.setRGB(i, j, 0);
rec[j][i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
return binaryImg;
}
相应的,在Gamestate类中提供构造函数来从图片生成游戏,GenerateHint()将生成的提示记录在GameState成员变量中:
/**
* Generate game when image is specified, hint is generated.
*
* @param path image path
* @param gameSizeRow board length y
* @param gameSizeCol board length x
* @throws IOException input error
*/
GameState(String path, int gameSizeRow, int gameSizeCol) throws IOException {
BOARD_SIZE_ROW = gameSizeRow;
BOARD_SIZE_COL = gameSizeCol;
board = new CellState[BOARD_SIZE_ROW][BOARD_SIZE_COL];
GenerateGameFromImg(path);
GenerateHint();
}
GameState类如下, hintRow记录行提示, hintCol记录列提示, board为一个enum CellState的二维数组:
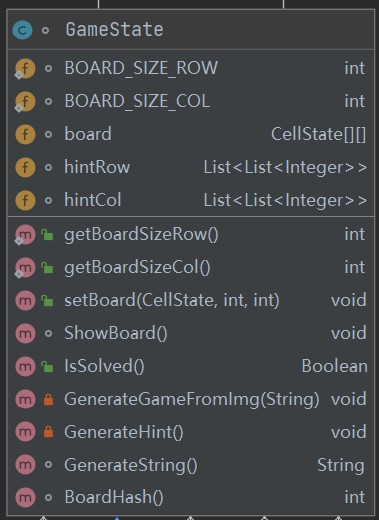
类构造函数有两个重载, 一个从图片生成游戏,一个从游戏提示生成游戏。单元格状态包括三种:空, 填, 不确定,使用enum类CellState
enum CellState {
FILLED,
EMPTY,
UNKNOWN
}
-
GenerateHint从board计算hint并存入类成员变量hintRow和hintCol -
GenerateString返回board的字符串表示, 0表示空, 1表示填色, 2表示不确定 -
BoardHash返回board的哈希值(Arrays.deepHashCode), 用于dfs剪枝
游戏求解
游戏的求解主要在两个类中实现, 即Solver和SolveGame
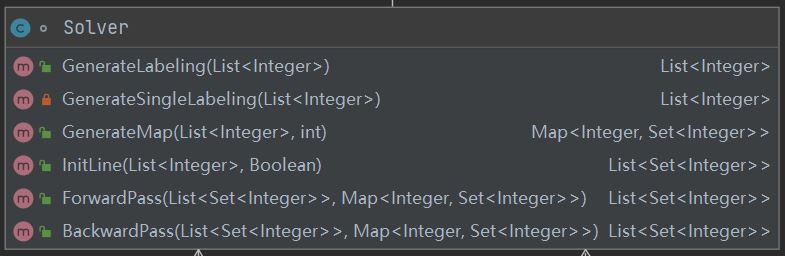
Solver类:
这个类中为求解所需要的各种操作, 包括生成标签,映射,向前和向后传播。
其中主要的函数GenerateMap生成每个标签与可能在其之前/之后出现的标签的映射,实现如下:
/**
* Generate a map of labeling, shift labeling by 1 or -1.
* For example:
* [-1, -1, 2, 3, 4, -5, -5, 6, 7, -8, -8] can be shifted by 1 to get a forward map
* [-1, 2, 3, 4, -5, -5, 6, 7, -8, -8]
* map: -1->-1, -1->2, 2->3, 3->4, ... -5->(-5,6), ...
*
* @param hint hint list of one line
* @param shift size of shift. Requires [-1, 1]
* @return map
* a map indicate what number can appear after/before cell n
*/
public Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> GenerateMap(List<Integer> hint, int shift) {
List<Integer> labeling = GenerateLabeling(hint);
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < labeling.size(); i++) {
int tmp_label = labeling.get(i);
int nxt_label; // shifted labeling
// get shifted label if exists
try {
nxt_label = labeling.get(i + shift);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
continue; // no corresponding label, ignore
}
// add shifted label to current label's map set
if (map.containsKey(tmp_label)) { // add to set
map.get(tmp_label).add(nxt_label);
} else { // initialize a set
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(nxt_label);
map.put(tmp_label, set);
}
} // end for
return map;
}
ForwardPass实现如下, available记录每个单元格之后可能出现的标签集合, 遍历当前单元格标签,得到每个标签映射后的标签,取并集:
/**
* Forward pass one line, get possible next cell's labels by mapping current cell's labels, intersect them
*
* @param lineSet list of sets in one line
* @param map map of labels of this line
* @return lineSet
* list of sets after forward pass, each set contains the labels that could appear in one cell
*/
public List<Set<Integer>> ForwardPass(List<Set<Integer>> lineSet, Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map) {
Set<Integer> available = new HashSet<>();
for (Set<Integer> set : lineSet) {
if (!available.isEmpty()) { // not first one
set.retainAll(available); // intersect with available label
available.clear();
}
for (int i : set) {
available.addAll(map.get(i)); // available labels of next cell
}
}
return lineSet;
}
SolveGame类:
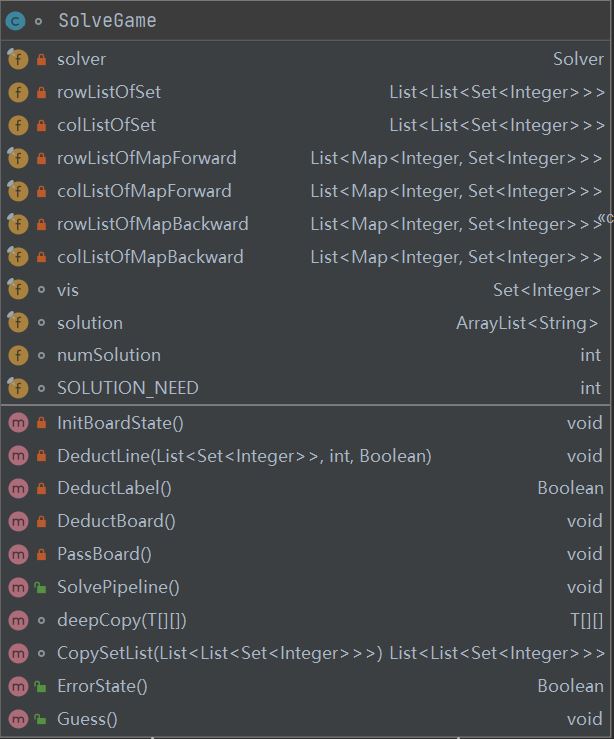
这个类实际求解游戏, 记录求解所需信息及结果。其需要记录的信息包括:
rowListOfSet: 行方向的标签集合,每个单元格有一个Set, 每行为Set的List,所有行即为Set的List的ListcolListOfSet: 列方向的标签集合rowListOfMapForward:行方向的标签映射,每行为Map的Listvis: String集合, 记录棋盘的哈希值solution: 记录所有找到的解的字符串表示numSolution: 找到的解的个数SOLUTION_NEED: 解个数上限,对于较大的游戏,可能存在很多解,默认只找到前50个
函数:
InitBoardState: 初始化标签集合和映射关系DeductBoard: 填充只有正/负标签的单元格DeductLabel: 削减被填充的单元格标签,返回boolean表示是否有标签被削减PassBoard: 进行向前,向后传播SolvePipeline: 确定性求解,包含上面三个过程Guess: dfs求解
SolvePipeline:
/**
* Solve pipeline, run until no cell changes state, it's deterministic
*/
public void SolvePipeline() {
Boolean changed = Boolean.TRUE;
while (changed) {
DeductBoard();
changed = DeductLabel();
PassBoard();
}
}
Guess:
/**
* For game with multiple solutions, guess is needed, use dfs search
*/
public void Guess(){
if(vis.contains(BoardHash())){ // board occurred
return;
} else {
vis.add(BoardHash()); // mark board as visited
}
if(IsSolved()){
numSolution ++;
String s = GenerateString();
System.out.println("solution " + numSolution + ":" + s);
solution.add(s); // record solution by string representation
ShowBoard();
return;
}
// find unknown cells
for(int i = 0; i < BOARD_SIZE_ROW; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < BOARD_SIZE_COL; j++){
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(rowListOfSet.get(i).get(j));
if(set.size() > 1){
// store current state
CellState[][] recBoard = deepCopy(board);
List<List<Set<Integer>>> recRowListOfSet = CopySetList(rowListOfSet);
List<List<Set<Integer>>> recColListOfSet = CopySetList(colListOfSet);
// loop possible value of one cell
for(int k: set){
rowListOfSet.get(i).get(j).clear();
rowListOfSet.get(i).get(j).add(k);
SolvePipeline();
Guess(); // recursive call
// there might be hundreds of solutions, comment this line to find them all
// it can be time consuming, make sure the amount of solution is limited
// 50(default) solution is enough for most cases
if(numSolution >= SOLUTION_NEED)return;
// drop changed lists and rollback, let garbage collector do the job
rowListOfSet = recRowListOfSet;
colListOfSet = recColListOfSet;
board = recBoard;
} // end label value for
}
} // end col for
}// end row for
}
至此,主要的程序实现说明就结束了,JavaDoc在file文件夹中。下面简要说一下测试及性能。
测试
测试主要针对Solver类和SolveGame类
SolverTest
GenerateLabeling:
测试包含空行, 满行及任意其他情况
// covers hint = [1]
@Test
void TestLabeling1(){
List<Integer> hint = new ArrayList<>();
hint.add(1);
List<Integer> labeling;
labeling = Arrays.asList(-1,-1,2,-3,-3);
assertEquals(labeling, solver.GenerateLabeling(hint));
}
GenerateMap分别测试-1,1偏移, hint如上包含不同情况
// covers shift = -1
// map {-1=[-1], 2=[-1], 3=[2], 4=[3], -5=[4, -5], 6=[-5], 7=[6], 8=[7], 9=[8], -10=[9, -10]}
@Test
void TestGenerateMapPrevious(){
List<Integer> hint;
hint = Arrays.asList(3, 4);
System.out.println(solver.GenerateMap(hint, -1));
}
InitLine也针对hint进行测试,覆盖不同参数isRow布尔值:
// covers hint = []
@Test
void TestInitLineEmpty(){
ArrayList<Integer> hint = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(solver.InitLine(hint, Boolean.FALSE));
}
// covers hint = [1]
@Test
void TestInitLineOne(){
ArrayList<Integer> hint = new ArrayList<>();
hint.add(1);
System.out.println(solver.InitLine(hint, Boolean.TRUE));
}
// covers hint = [10]
@Test
void TestInitLineFull(){
ArrayList<Integer> hint = new ArrayList<>();
hint.add(10);
System.out.println(solver.InitLine(hint, Boolean.FALSE));
}
ForwardPass:
@Test
void forwardPass() {
List<Integer> hint = new ArrayList<>();
hint.add(3);
hint.add(4);
List<Integer> labeling = solver.GenerateLabeling(hint);
List<Set<Integer>> lineSet = solver.InitLine(hint, Boolean.FALSE);
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = solver.GenerateMap(labeling, 1);
lineSet.get(0).remove(2);
List<Set<Integer>> lineSetPassed = solver.ForwardPass(lineSet, map);
System.out.println(lineSetPassed);
}
SolveGameTest
直接从图片生成hint,再求解,比对二者board是否一致,多个解的测试主要记录时间
// square board
@Test
public void CombinedTestSquare() throws IOException {
GameState state = new GameState("D:/learn/2020_9/software/img/einstein.jpg",
50, 50);
SolveGame solveGame = new SolveGame(state.hintRow, state.hintCol,
50, 50);
SolveAndClock(state, solveGame);
}
// rectangle board
@Test
public void CombinedTestRec() throws IOException {
GameState state = new GameState("D:/learn/2020_9/software/img/einstein.jpg",
50, 51);
SolveGame solveGame = new SolveGame(state.hintRow, state.hintCol,
50, 51);
SolveAndClock(state, solveGame);
}
// multiple solutions 40*40
@Test
public void CombinedTestMultiMid() throws IOException {
GameState state = new GameState("D:/learn/2020_9/software/img/einstein.jpg",
40, 40);
SolveGame solveGame = new SolveGame(state.hintRow, state.hintCol,
40, 40);
GuessAndClock(state, solveGame);
}
// multiple solutions 100*70
@Test
public void CombinedTestMultiRec() throws IOException {
GameState state = new GameState("D:/learn/2020_9/software/img/einstein.jpg",
100, 70);
SolveGame solveGame = new SolveGame(state.hintRow, state.hintCol,
100, 70);
GuessAndClock(state, solveGame);
}
private void SolveAndClock(GameState state, SolveGame solveGame) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
solveGame.SolvePipeline();
if(solveGame.ErrorState()){
System.out.println("Not valid game!");
return;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long duration = (endTime - startTime)/1000000; //divide by 1000000 to get milliseconds.
System.out.println("solve completed in " + duration + "ms");
assertArrayEquals(state.board, solveGame.board);
}
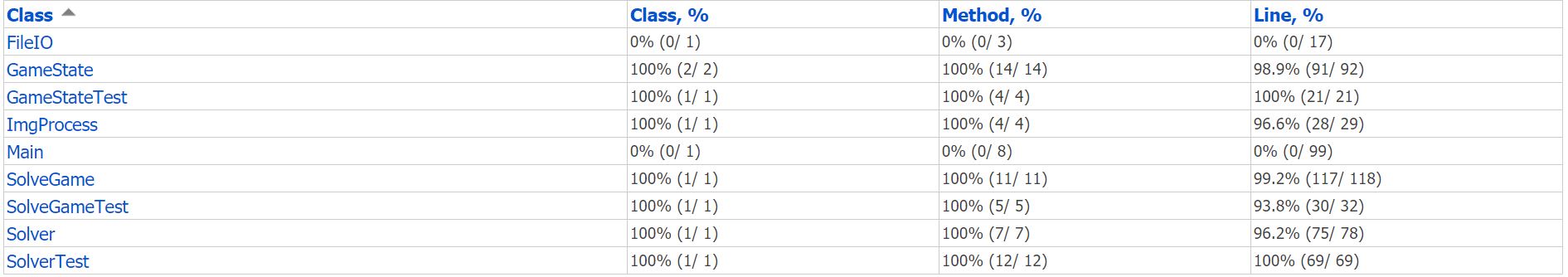
详细coverage report在file文件夹中
性能
测试了不同规模的游戏求解时间,第二列为确定性求解时间,第三列dfs找到50个解的总时间受未确定的单元格数量影响较大,有些图片生成的游戏可能随规模增大不确定格数增加,这里仅作为参考。
| board size | deterministic solver | dfs 50 solutions |
|---|---|---|
| 10*5 | 0.008 s | None |
| 40*40 | 0.27 s | None |
| 50*50 | 0.45 s | None |
| 100*70 | 0.68 s | 6.98 s |
| 100*100 | 0.93 s | 12.43 s |
| 200*100 | 1.68 s | 21.73 s |
| 200*200 | 5.28 s | 95.59 s |
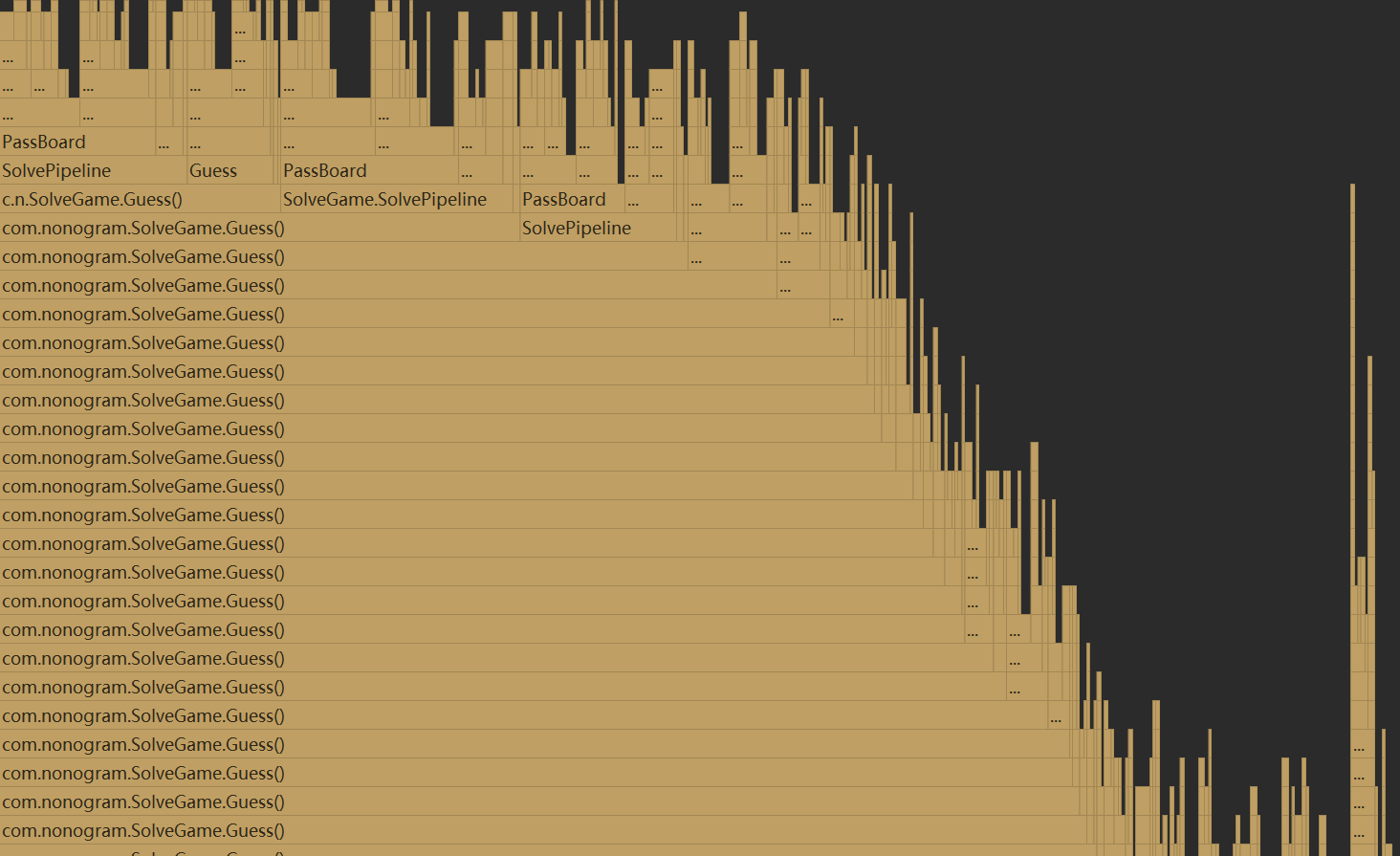
唯一解游戏的flame graph:
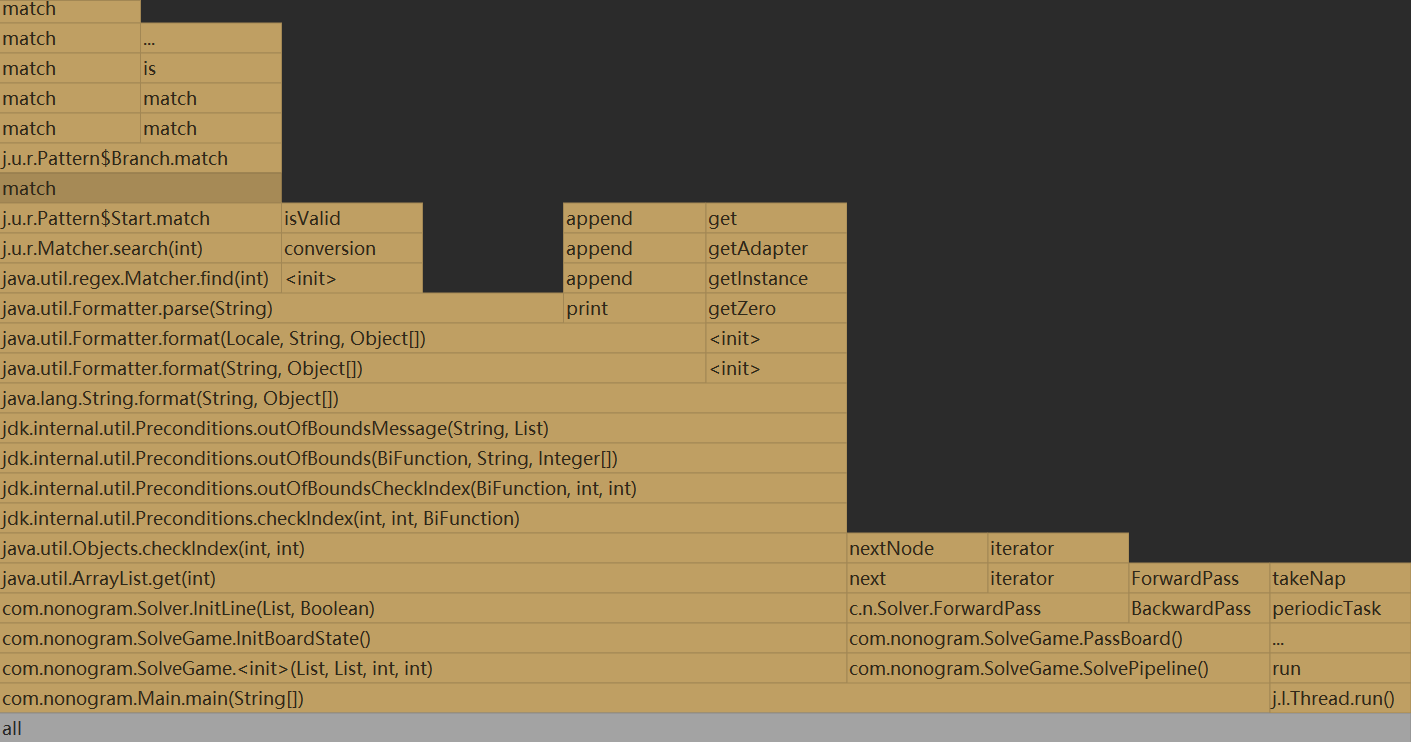
不唯一:
主要在于dfs的不断调用